Note of Opencv to Python Opencv 在Pycharm中的配置 1 2 3 pip install opencv-python pip install opencv-contrib-python pip install pytesseract
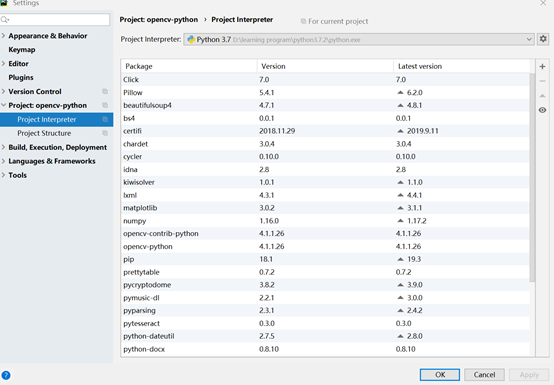
新建python项目,注意解释器正确配置应该如下:
常见图像坐标系 Opencv:
Matlab:
基本操作 将照片读入到矩阵中,并显示 1 2 3 4 5 6 src = cv.imread("D:/IMG_20161227_154705.jpg" ) cv.imshow("input" , src) cv.waitKey(0 ) 必须要有 cv.imwrite("D:/result.jpg" , gray) cv.waitKey(0 ) cv.destroyAllWindows()
cv.IMREAD_COLOR:读入一副彩色图像,将其转换为BGR模式,图像的透明度会被忽略,这是默认参数。
cv.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE:以灰度模式读入图像
cv.IMREAD_UNCHANGED:读入一幅图像,并且包括图像的alpha 通道
cv.IMREAD_ANYDEPTH : 若设置返回相应深度图像(16位/32位),否则将其转换为8位
IMREAD_LOAD_GDAL :使用gda驱动载入图像
可使用python自带的Matplotlib显示图像。但注意opencv为BGR,Matplotlib为RGB,被opencv的imread读入后,不能被Matplotlib显示.
imwrite要求图像为BGR或灰度格式,并且每个通道有一定的位,BMP每通道8位,PNG每通道8位/16位
图像与原始字节之间的转换 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 import osrandombytearray = bytearray(os.urandom(120000 )) nparray = np.array(randombytearray) grayimage = nparray.reshape((300 , 400 )) bgrimage = nparray.reshape([100 , 400 , 3 ]) src = np.random.randint(0 , 255 , 120000 ).reshape(300 , 400 ) print(src)
窗口操作 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 cv.namedWindow("input" , cv.WINDOW_AUTOSIZE) 适应图片大小 cv.WINDOW_NORMAL 窗口大小可调节 CV_WINDOW_OPENGL 支持OpenGL namedWindow()创建一个窗口。imshow可以直接指定窗口名,可以省去此函数(默认调用),但如果显示图像之前需要其他窗口操作时,需要调用此函数 destroyWindow() 关闭特定窗口 destroyAllWindows()关闭所有的HighGUI窗口 cv.startWindowThread()
在调用cv.startWindowThread();后,即使没有调用waitKey()函数,图片也依然实时刷新。opencv的imshow()函数调用以后,并不立即刷新显示图片,而是等到waitKey()后才会刷新图片显示,所以cv.startWindowThread();是新开一个线程实时刷新图片显示。
waitKey函数 1.waitKey()返回的为-1(没有键被按下)或ASCII码值,
2.使用OpenCV的imshow函数显示图片,必须配合waitKey 函数使用,才能将图片显示在windows窗体上。否则,imshow 函数单独使用只能弹出空白窗体,而无法显示图片。
3.waitKey的时间延迟,只对Windows窗体有效,而且是 namedWindow 函数创造的OpenCV窗体,对于MFC或者Qt这种GUI窗体是否有效是一种未知结果,
不设置参数 :特定的几毫秒之内,如果按下任意键,这个函数会返回按键的ASCII 码值,程序将会继续运行。如果没有键盘输入,返回值为-1
ASCII码值 :0~127,共128个
设置参数 :使用waitKey(0) (无限等待)来判断相应按键操作,若为64位电脑,则需设置为k=cv2.waitKey(0)&0xFF。
3.真正能起到程序暂停的作用的是我们熟悉的Windows API函数Sleep
1 2 3 4 5 6 k = cv2.waitKey(0 )&0xFF if k == 27 : cv2.destroyAllWindows() elif k == ord('s' ): cv2.imwrite('messigray.png' ,img) cv2.destroyAllWindows()
视频与电脑摄像头输入、存储 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 def video_demo () : capture = cv.VideoCapture(0 ) fourcc = cv.VideoWriter_fourcc(*'XVID' ) out = cv2.VideoWriter('output.avi' ,fourcc, 20.0 , (640 ,480 )) if capture.isOpened() == 1 : print("camera has been initialized correctly" ) elif capture.isOpened() == 0 : print("camera has not been initialized correctly" ) ret, frame = capture.read() while (True ): ret, frame = capture.read() frame1 = cv.flip(frame, 1 ) frame2 = cv.transpose(frame) cv.imshow("video" , frame) cv.imshow("video1" , frame1) out.write(frame1) print(capture.get(3 )) cv.imshow("video2" , frame2) c = cv.waitKey(1 ) if c & oxFF ==ord('q' ) capture.release() break
cv.VideoCapture为一个类,get(CV_CAP_PROP_FPS)可返回视频帧速率的准确值,但不能返回摄像头帧速率的准确值(总是返回0),可使用计时器来测量
视频写入时FourCC码以cv.FOURCC(‘M’,’J’,’P’,’G’) 或者cv.FOURCC(*’MJPG’)传给fourcc,编码格式如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 cv2.VideoWriter_fourcc('I','4','2','0'): This option is an uncompressed YUV encoding, 4:2:0 chroma subsampled. This encoding is widely compatible but produces large files. The file extension should be .avi. • cv2.VideoWriter_fourcc('P','I','M','1'): This option is MPEG-1. The file extension should be .avi. • cv2.VideoWriter_fourcc('X','V','I','D'): This option is MPEG-4 and a preferred option if you want the resulting video size to be average. The file extension should be .avi. • cv2.VideoWriter_fourcc('T','H','E','O'): This option is Ogg Vorbis. The file extension should be .ogv. • cv2.VideoWriter_fourcc('F','L','V','1'): This option is a Flash video. The file extension should be .flv.
从文件播放视频时,使用cv.waiKey() 设置适当的持续时间,一般25ms合适,设置地高的话,视频播放地慢
cap.read() :若帧读取正确,返回True,检查其返回值判断视频文件是否到结尾
cap.isOpened() :摄像头成功初始化,返回True,否则使用cap.open()
cap.get(propId) :获得视频的参数信息,propId 可以是0 到18 之间的任何整数,见下表:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 • CV_CAP_PROP_POS_MSEC • CV_CAP_PROP_POS_FRAMES • CV_CAP_PROP_POS_AVI_RATIO • CV_CAP_PROP_FRAME_WIDTH • CV_CAP_PROP_FRAME_HEIGHT • CV_CAP_PROP_FPS • CV_CAP_PROP_FOURCC • CV_CAP_PROP_FRAME_COUNT • CV_CAP_PROP_FORMAT • CV_CAP_PROP_MODE • CV_CAP_PROP_BRIGHTNESS • CV_CAP_PROP_CONTRAST • CV_CAP_PROP_SATURATION • CV_CAP_PROP_HUE • CV_CAP_PROP_GAIN • CV_CAP_PROP_EXPOSURE • CV_CAP_PROP_CONVERT_RGB • CV_CAP_PROP_WHITE_BALANCE • CV_CAP_PROP_RECTIFICATION
cap.set(propId,value):修改视频参数,value为新值
3—width,4—hight
使用一组摄像头时:
1 2 3 4 5 success0 = cameraCapture0.grab() success1 = cameraCapture1.grab() if success0 and success1: frame0 = cameraCapture0.retrieve() frame1 = cameraCapture1.retrieve()
获取图片的信息 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 def get_image_info (image) : print(type(image)) print(image.shape) print(image.size) print(image.dtype) pixel_data = np.array(image) print(image) 可以直接打印
绘图功能 img:想要绘图的图像
color:BGR模式输入
thickness:默认为1,对于封闭图形设置为-1可实现填充
lineType:8连接,抗锯齿型连接(平滑性好,cv2.LINE_AA)
shift:坐标点与数轴的精度,默认为0
后五个参数的顺序一般如上
Drawing Line:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 img = np.zeros((512 ,512 ,3 ), np.uint8) img = cv2.line(img,(0 ,0 ),(511 ,511 ),(255 ,0 ,0 ),5 ) img = cv2.rectangle(img,(384 ,0 ),(510 ,128 ),(0 ,255 ,0 ),3 ) img = cv2.circle(img,(447 ,63 ), 63 , (0 ,0 ,255 ), -1 ) img = cv2.ellipse(img,(256 ,256 ),(100 ,50 ),0 ,0 ,180 ,(255 , 0 , 0 ),-1 ) pts = np.array([[10 ,5 ],[20 ,30 ],[70 ,20 ],[50 ,10 ]], np.int32) pts = pts.reshape((-1 ,1 ,2 )) img = cv2.polylines(img,[pts],True ,(0 ,255 ,255 )) font = cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX cv2.putText(img,'OpenCV' ,(10 ,500 ), font, 4 ,(255 ,255 ,255 ),2 ,cv2.LINE_AA)
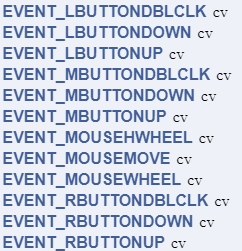
鼠标操作响应 事件列表:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 def draw_circle (event,x,y,flags, param) : if event == cv.EVENT_LBUTTONDBLCLK: cv.circle(img, [x, y], 10 , (255 , 0 , 0 ), -1 ) img = np.zeros((512 , 512 , 3 ), np.uint8) cv.namedWindow('image' ) cv.setMouseCallback('image' , draw_circle) while (1 ): cv.imshow('image' ,img) if cv.waitKey(20 ) & 0xFF == 27 : break cv.destroyAllWindows()
通过按键来控制不同的鼠标事件响应:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 drawing = False mode = True ix, iy = -1 , -1 def draw_circle (event,x,y,flags,param) : global ix, iy, drawing, mode if event == cv.EVENT_LBUTTONDOWN: drawing=True ix, iy = x, y elif event == cv.EVENT_MOUSEMOVE and flags == cv.EVENT_FLAG_LBUTTON: if drawing == True : if mode == True : cv.rectangle(img,(ix,iy),(x,y),(0 ,255 ,0 ),-1 ) else : r=int(np.sqrt((x-ix)**2 +(y-iy)**2 )) cv.circle(img,(ix,iy),r,(0 ,0 ,255 ),-1 ) elif event == cv.EVENT_LBUTTONUP: drawing=False img = np.zeros((512 , 512 , 3 ), np.uint8) cv.namedWindow('image' ) cv.setMouseCallback('image' ,draw_circle) while (1 ): cv.imshow('image' , img) k = cv.waitKey(1 ) & 0xFF if k == ord('m' ): mode = not mode elif k == 27 : break cv.destroyAllWindows()
opencv有限的事件处理能力与GUI处理能力,将其集成到其他应用程序框架更受欢迎
滑动条的实现 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 import cv2import numpy as npdef nothing (x) : pass img=np.zeros((300 ,512 ,3 ),np.uint8) cv2.namedWindow('image' ) cv2.createTrackbar('R' ,'image' ,0 ,255 ,nothing) cv2.createTrackbar('G' ,'image' ,0 ,255 ,nothing) cv2.createTrackbar('B' ,'image' ,0 ,255 ,nothing) switch='0:OFF\n1:ON' cv2.createTrackbar(switch,'image' ,0 ,1 ,nothing) while (1 ): cv2.imshow('image' ,img) k=cv2.waitKey(1 )&0xFF if k==27 : break r=cv2.getTrackbarPos('R' ,'image' ) g=cv2.getTrackbarPos('G' ,'image' ) b=cv2.getTrackbarPos('B' ,'image' ) s=cv2.getTrackbarPos(switch,'image' ) if s==0 : img[:]=0 else : img[:]=[b,g,r] cv2.destroyAllWindows()
核心操作 色彩空间转换 1 2 3 4 gray = cv.cvtColor(src, cv.COLOR_BGR2GRAY) dst = cv.bitwise_not(image) gray = cv.cvtColor(image, cv.COLOR_BGR2GRAY) back_rgb = cv.cvtColor(gray, cv.COLOR_GRAY2BGR)
灰度:去除彩色信息将其转换成灰阶,对人脸检测等中间处理特别有效
HSV:H(Hue)色调,S(Saturation)饱和度,V(Value)表示黑暗程度或光谱另一端的明亮程度,便于色彩区分 ,opencv中将hue值设为0-180,便于用uint8表示
Print函数Tips 1 2 3 4 打印变量值 print("width : %s, height : %s channels : %s" % (width, height, channels)) 打印矩阵 print(image)
遍历像素点 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 def access_pixels (image) : height = image.shape[0 ] width = image.shape[1 ] channels = image.shape[2 ] print("width : %s, height : %s channels : %s" % (width, height, channels)) for row in range(height): for col in range(width): for c in range(channels): pv = image[row, col, c] image[row, col, c] = 255 – pv cv.imshow("demo" , image)
优先使用索引等方法对像素点、面进行操作,使用循环会使得效率低下,尤其对于视频处理
矩阵操纵(创建一幅图像) ones创建任意维度和元素个数的数组,其元素值均为1
1 2 3 4 5 6 zeros([m,n…],int8) 创建任意维度和元素个数的数组,其元素值均为0 img = np.zeros([400 , 400 , 3 ], np.uint8) matrix = np.ones([6 , 6 ], np.float32)
fill用来填充矩阵,
cv.convertScaleAbs() 可以将浮点数转化为uint8 ,负数转换为绝对值
1 m2 = matrix.reshape([3 , 12 ])
array生成任意矩阵,可以作为算子
1 m3 = np.array([[1,2,3], [4,5,6], [7,8,9]],np.int32)
获取程序执行时间 1 2 3 4 5 t1 = cv.getTickCount() create_image() t2 = cv.getTickCount() time = (t2 - t1) / cv.getTickFrequency() print("time = %s ms" % (time * 1000 ))
可以通过调用opencv自带的API来减少程序执行时间
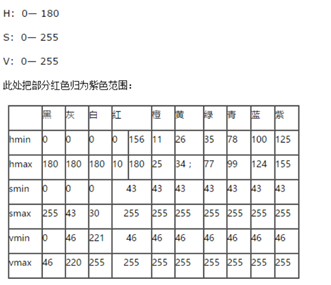
提取某颜色对应的像素 思路:转换到HSV空间,再参考下表设置inRange函数的参数(红色设置为第二列较佳)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 def extract_object_demo () : capture = cv.VideoCapture("D:/IMG_9764.MP4" ) while (True ): ret, frame = capture.read() if ret == False : break hsv = cv.cvtColor(frame, cv.COLOR_BGR2HSV) lower_hsv = np.array([0 , 43 , 46 ]) upper_hsv = np.array([10 , 255 , 255 ]) mask = cv.inRange(hsv, lowerb=lower_hsv, upperb=upper_hsv) dst = cv.bitwise_and(frame, frame, mask=mask) cv.imshow("video" , frame) cv.imshow("mask" , dst) c = cv.waitKey(50 ) if c == 27 : break
图像通道的合并、分离、单通道操作、单像素操作 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 b, g, r = cv.split(src) cv.imshow("blue" , b) cv.imshow("green" , g) cv.imshow("red" , r) src = cv.merge([b, g, r]) src[:, :, 0 ] = 0 src.itemset((150 , 120 , 0 ), 255 ) print(src.itemset((150 , 120 , 0 ))) cv.imshow("changed image" , src) h, w = src.shape[0 :2 ] print(src[30 , 30 , :])
图像算术运算、逻辑运算 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 dst = cv.add(m1, m2) dst = cv.subtract(m1, m2) dst = cv.divide(m1, m2) dst = cv.multiply(m1, m2) M1 = cv.mean(m1) M2, dev2 = cv.meanStdDev(m2) Tips:方差越小,则该图片包含的信息越少,可设置阈值来过滤无意义的图片 dst1 = cv.bitwise_or(m1, m2) dst2 = cv.bitwise_and(m1, m2) dst3 = cv.bitwise_not(m1)
调整对比度和亮度 1 2 3 4 5 6 def contrast_brightness_demo (image, c, b) : h, w, ch = image.shape blank = np.zeros([h, w, ch], image.dtype) dst = cv.addWeighted(image, c, blank, 1 -c, b) cv.imshow("con_bri_demo" , dst) 像素运算式:dst = src1*alpha + src2*beta + gamma
ROI选择 1 2 3 4 5 face = src[50 :250 , 100 :300 ] gray = cv.cvtColor(face, cv.COLOR_BGR2GRAY) backrgb = cv.cvtColor(gray, cv.COLOR_GRAY2BGR) src[50 :250 , 100 :300 ] = backrgb cv.imshow("face" , src)
图像处理 泛洪填充 1 2 3 4 5 6 def fill_color_demo (image) : copyImg = image.copy() h, w = image.shape[:2 ] mask = np.zeros([h+2 , w+2 ], np.uint8) cv.floodFill(copyImg, mask, (30 , 30 ), (0 , 255 , 255 ), (100 , 100 , 100 ), (50 , 50 , 50 ), cv.FLOODFILL_FIXED_RANGE) cv.imshow("fill_color_demo" , copyImg)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 def fill_binary () : image = np.zeros([400 , 400 , 3 ], np.uint8) image[100 :300 , 100 :300 , :] = 255 cv.imshow("fill_binary" , image) mask = np.ones([402 , 402 , 1 ], np.uint8) mask[100 :300 , 100 :300 ] = 0 cv.floodFill(image, mask, (200 , 200 ), (255 , 255 , 0 ), cv.FLOODFILL_MASK_ONLY) cv.imshow("filled binary" , image)
图像模糊(图像平滑) 概述 低通滤波:去噪,模糊图像,但去除了高频成分(噪声、边界)
高通滤波(图像梯度):找到边缘
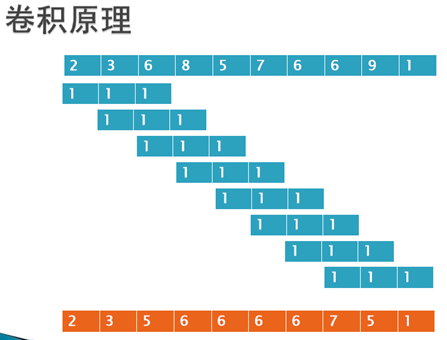
空间滤波的数学原理:二维空间卷积
分类及应用场景 平均:卷积框覆盖区域所有像素的平均值来代替中心元素
高斯(低通滤波器之一):方框中心的值最大,其余方框根据距离中心元素的距离递减,构成一个高斯小山包。原来的求平均数现在变成求加权平均数,权就是方框里的值,X与y方向的标准差相等,若设置为0,则函数根据核的大小自动计算
1 2 blur = cv2.GaussianBlur(img,(5 ,5 ),0 )
只考虑像素之间的空间关系,而不会考虑像素值之间的关系(像素的相似度)
中值:用与卷积框对应像素的中值来替代中心像素的值,去除椒盐噪声、数字化的视频噪声尤其是彩色图像的噪声,但对于较大ksize,代价较高
双边:保持边界清晰的情况下有效的去除噪音,使用空间高斯权重(位置差异越小权重越大)与灰度值相似性高斯权重(灰度值差异越小权重越大),边缘处灰度值与中心像素灰度值相比变化大,权重小不会被模糊
1 2 blur = cv2.bilateralFilter(img,9 ,75 ,75 )
关于算子:元素个数为奇数(奇数行奇数列),总和为0 :进行边缘和梯度计算,
总和为1 :进行增强锐化等,相当于将感兴趣像素与其邻近像素值间的差放大,图像的亮度没有改变
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 dst = cv.blur(image, (1 , 15 )) dst = cv.medianBlur(image, 5 ) def custom_blur_demo (image) : kernel = np.array([[0 , -1 , 0 ], [-1 , 5 , -1 ], [0 , -1 , 0 ]], np.float32) dst = cv.filter2D(image, -1 , kernel=kernel) cv.imshow("custom_blur_demo" ,dst)
filter2D()对每个通道使用相同的核,若要每个通道的核不同,则使用split分离通道,再用merge合并
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 from scipy import ndimagekernel_3x3 = np.array([[-1 , -1 , -1 ], [-1 , 8 , -1 ], [-1 , -1 , -1 ]]) k3 = ndimage.convolve(img, kernel_3x3)
图像梯度 二维函数的梯度定义为向量,其幅度即模如下:
可由绝对值来近似:
离散化表示:
Laplacian 算子 可用来计算图像的二阶导数,推导在Matlab图像坐标系下进行:
第二个算子为考虑了对角线元素的效果
1 2 #cv2.CV_64F 输出图像的深度(数据类型),可以使用-1, 与原图像保持一致np.uint8 laplacian=cv2.Laplacian(img,cv2.CV_64F)
Prewitt算子 对角线方向:
Sobel算子和Scharr算子 Sobel 算子是高斯平滑与微分操作的结合体,所以它的抗噪声能力很好。你可以设定求导的方向(xorder 或yorder)。还可以设定使用的卷积核的大小(ksize)。如果ksize=-1,会使用3x3 的Scharr 滤波器,它的的效果要比3x3 的Sobel 滤波器好(而且速度相同,所以在使用3x3 滤波器时应该尽量使用Scharr 滤波器)。3x3 的
Sobel算子的卷积核:
Scharr 滤波器卷积核如下:
X方向:
Y方向:
1 2 3 4 sobelx=cv2.Sobel(img,cv2.CV_64F,1 ,0 ,ksize=5 ) sobely=cv2.Sobel(img,cv2.CV_64F,0 ,1 ,ksize=5 )
当我们可以通过参数 -1 来设定输出图像的深度(数据类型)与原图像保持一致,但是我们在代码中使用的却是 cv2.CV_64F。这是为什么呢?想象一下一个从黑到白的边界的导数是正数,而一个从白到黑的边界点导数却是负数。如果原图像的深度是np.int8 时,所有的负值都会被截断变成 0,换句话说就是把把边界丢失掉。所以如果这两种边界你都想检测到,最好的的办法就是将输出的数据类型设置的更高,比如 cv2.CV_16S,cv2.CV_64F 等。取绝对值然后再把它转回到 cv2.CV_8U
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 sobelx8u = cv2.Sobel(img,cv2.CV_8U,1 ,0 ,ksize=5 ) sobelx64f = cv2.Sobel(img,cv2.CV_64F,1 ,0 ,ksize=5 ) abs_sobel64f = np.absolute(sobelx64f) sobel_8u = np.uint8(abs_sobel64f)
边缘检测 Laplacian(),sobel,scharr等会将噪声错误地识别为边缘,故在此之前应进行中值滤波和灰度化
核的元素值之和为0,将边缘转为白色,非边缘转为黑色
Canny边缘检测 John F.Canny 在1986 年提出的,分为以下五步:
使用高斯滤波器去噪
使用Sobel算子计算水平方向和垂直方向梯度,找到边界的梯度和方向
梯度的方向一般总是与边界垂直。梯度方向被归为四类:垂直,水平,和两个对角线
3.在边缘上使用非最大抑制(NMS)
在获得梯度的方向和大小之后,应该对整幅图像做一个扫描,去除那些非边界上的点。对每一个像素进行检查,看这个点的梯度是不是周围具有相同梯度方向的点中最大的。
4.检测到的边缘上使用双阈值去除假阳性:
当图像的灰度梯度高于maxVal 时被认为是真的边界,那些低于minVal 的边界会被抛弃。如果介于两者之间的话,就要看这个点是否与某个被确定为真正的边界点相连,如果是就认为它也是边界点,如果不是就抛弃
5.分析所有边缘及其间的连接,保留真正的边缘,消除不明显的边缘
函数实现:cv2.Canny()
第一个参数是输入图像。第二和第三个分别是minVal 和maxVal。第三个参数设置用来计算图像梯度的Sobel
1 img=cv2.Canny(img, 50 , 150 , apertureSize=3 , L2gradient=True )
用滑动条观看阈值对检测效果的影响:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 def nothing (x) : pass img = cv2.imread("../images/statue_small.jpg" , 1 ) cv2.namedWindow('canny' ) cv2.createTrackbar('minval' ,'canny' ,0 ,255 , nothing) cv2.createTrackbar('maxval' ,'canny' ,0 ,255 , nothing) while (1 ): minval = cv2.getTrackbarPos('minval' ,'canny' ) maxval = cv2.getTrackbarPos('maxval' ,'canny' ) canny = cv2.Canny(img, minval, maxval) cv2.imshow("image" , img) cv2.imshow("canny" , canny) k = cv2.waitKey(0 ) if k == 27 : break cv2.destroyAllWindows()
轮廓检测 轮廓可以简单认为成将连续的点(连着边界)连在一起的曲线,具有相同的颜色或者灰度 。轮廓在形状分析和物体的检测和识别中很有用。注意:
为更加准确,寻找轮廓前,进行阈值化或canny边缘检测
cv2.findContours()会修改原始图像,若后续想使用原始图像,应使用copyImg = image.copy()查找轮廓是在黑色背景中找白色物体
应用 计算多边形边界、形状逼近、计算感兴趣区域
在opencv4中cv2.findContours输入 :第一个是输入图像,第二个是轮廓检索模式,第三个是轮廓近似方法,cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_NONE所有边界点均被存储,cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE去掉轮廓上的冗余点。压缩轮廓,减少内存开支
返回 :只返回轮廓(python列表,每个元素为一个numpy数组)、轮廓的层析结构、不返回图像
轮廓的绘制 cv2.drawContours()输入:原始图像、轮廓、轮廓的索引(设置为-1时绘制所有轮廓、轮廓的颜色、轮廓的厚度,输出:图像
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 import numpy as npimport cv2.cv2im = cv2.imread('D:/opencv_imagedata/data/shape_binary.png' ) imgray = cv2.cvtColor(im,cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY) ret,thresh = cv2.threshold(imgray,127 ,255 ,0 ) contours, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(thresh,cv2.RETR_TREE,cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_NONE) img1 = cv2.drawContours(im, contours, -1 , (255 ,0 ,0 ), 3 ) img2 = cv2.drawContours(im, contours, 3 , (0 ,255 ,0 ), 3 ) cv2.imshow("img2" ,img2) cv2.waitKey() cv2.destroyAllWindows()
轮廓特征 矩 1 2 3 4 5 cnt = contours[0] M = cv2.moments(cnt) print(M) cx = int(M['m10']/M['m00']) cy = int(M['m01']/M['m00'])
根据这些矩的值,我们可以计算出对象的重心:
轮廓面积 1 2 area = M['m00'] area = cv2.contourArea(cnt)
轮廓周长 1 perimeter = cv2.arcLength(cnt,True)
轮廓近似 1 2 3 epsilon = 0.1 *cv2.arcLength(cnt,True ) approx = cv2.approxPolyDP(cnt,epsilon,True ) img3 = cv2.drawContours(im, approx, 0 , (0 , 255 , 0 ), 3 )
cv2.approxPolyDP输入:轮廓、原轮廓与近似多边形周长的最大差值,输出与输入曲线类型相同的曲线
凸包 与轮廓近似相似凸性缺陷:一般来说,凸性曲线总是凸出来的,至少是平的。如果有地方凹进去了就被叫做凸性缺陷
1 hull = cv2.convexHull(points[, hull[, clockwise[, returnPoints]]
输入:
1 2 3 4 5 6 points 我们要传入的轮廓 hull 输出,通常不需要 clockwise 方向标志。如果设置为True,输出的凸包是顺时针方向的。 否则为逆时针方向。 returnPoints 默认值为True。它会返回凸包上点的坐标。如果设置 为False,就会返回与凸包点对应的轮廓上的点。
1 hull = cv2.convexHull(cnt)
如returnPoints设置为true返回[[[234 202]], [[ 51 202]], [[ 51 79]], [[234 79]]];设置为False返回[[129],[ 67],[ 0],[142]],可认为是cnt这个列表的索引
凸性检测 1 k = cv2.isContourConvex(cnt)
返回一个布尔值
边界矩形 直边界矩形 :没有旋转的矩形,矩形面积非最小
1 2 x,y,w,h = cv2.boundingRect(cnt) img = cv2.rectangle(img,(x,y),(x+w,y+h),(0,255,0),2)
旋转的边界矩形
考虑了对象的旋转,矩形面积最小,cv2.minAreaRect()返回的是一个Box2D 结构,其中包含矩形左上角角点的坐标(x,y),矩形的宽和高(w,h),以及旋转角度。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 for c in contours: # find bounding box coordinates x,y,w,h = cv2.boundingRect(cnt) cv2.rectangle(img, (x,y), (x+w, y+h), (0, 255, 0), 2) # find minimum area rect = cv2.minAreaRect(cnt) # calculate coordinates of the minimum area rectangle box = cv2.boxPoints(rect) # normalize coordinates to integers box = np.int0(box) # draw contours cv2.drawContours(img, [box], 0, (0,0, 255), 3)
最小闭圆(最小外接圆) 找到一个轮廓的外切圆
1 2 3 4 (x,y),radius = cv2.minEnclosingCircle(cnt) center = (int(x),int(y)) radius = int(radius) img = cv2.circle(img,center,radius,(0 ,255 ,0 ),2 )
椭圆拟合 返回旋转边界矩形的内切椭圆
1 2 ellipse = cv2.fitEllipse(cnt) img = cv2.ellipse(im,ellipse,(0,255,0),2)
直线拟合 根据轮廓上的点来拟合一条直线
1 2 3 4 5 [vx,vy,x,y] = cv2.fitLine(cnt, cv2.DIST_L2,0 ,0.01 ,0.01 ) rows, cols = im.shape[:2 ] lefty = int((-x*vy/vx) + y) righty = int(((cols-x)*vy/vx)+y) img4 = cv2.line(im,(cols-1 ,righty),(0 ,lefty),(0 ,255 ,0 ),2 )
轮廓的性质 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 x,y,w,h = cv2.boundingRect(cnt) aspect_ratio = float(w)/h area = cv2.contourArea(cnt) rect_area = w*h extent = float(area)/rect_area hull = cv2.convexHull(cnt) hull_area = cv2.contourArea(hull) solidity = float(area)/hull_area equi_diameter = np.sqrt(4 *area/np.pi) (x,y),(MA,ma),angle = cv2.fitEllipse(cnt) mask = np.zeros(imgray.shape,np.uint8) cv2.drawContours(mask,[cnt],0 ,255 ,-1 ) pixelpoints = np.transpose(np.nonzero(mask)) pixelpoints = cv2.findNonZero(mask) min_val, max_val, min_loc, max_loc = cv2.minMaxLoc(im,mask = mask) mean_color = cv2.mean(im,mask = mask) mean_graylevel = cv2.mean(im,mask = mask) leftmost = tuple(cnt[cnt[:,:,0 ].argmin()][0 ]) rightmost = tuple(cnt[cnt[:,:,0 ].argmax()][0 ]) topmost = tuple(cnt[cnt[:,:,1 ].argmin()][0 ]) bottommost = tuple(cnt[cnt[:,:,1 ].argmax()][0 ])
凸缺陷 cv2.convexityDefects返回每个凸缺陷的[起点,终点,最远的点,到最
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 import cv2import numpy as npimg = cv2.imread('star.jpg' ) img_gray = cv2.cvtColor(img,cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY) ret, thresh = cv2.threshold(img_gray, 127 , 255 ,0 ) contours,hierarchy = cv2.findContours(thresh,2 ,1 ) cnt = contours[0 ] hull = cv2.convexHull(cnt,returnPoints = False ) defects = cv2.convexityDefects(cnt,hull) for i in range(defects.shape[0 ]): s,e,f,d = defects[i,0 ] start = tuple(cnt[s][0 ]) end = tuple(cnt[e][0 ]) far = tuple(cnt[f][0 ]) cv2.line(img,start,end,[0 ,255 ,0 ],2 ) cv2.circle(img,far,5 ,[0 ,0 ,255 ],-1 ) cv2.imshow('img' ,img) cv2.waitKey(0 ) cv2.destroyAllWindows()
点与轮廓间的距离 求解图像中的一个点到一个对象轮廓的最短距离。如果点在轮廓的外部,返回值为负。如果在轮廓上,返回值为0。如果在轮廓内部,返回值为正。
第三个参数是measureDist。如果设置为True,就会计算最短距离。如果是False,只会判断这个点与轮廓之间的位置关系(返回值为+1,-1,0)
1 dist = cv2.pointPolygonTest(cnt,(50,50),True)
形状匹配 cv2.matchShape()比较两个形状或轮廓的相似度,返回值越小匹配越好
原理:Hu矩:Hu 矩是归一化中心矩的线性组合,之所以这样做是为了能够获取代表图像的某个特征的矩函数,这些矩函数对某些变化如缩放,旋转,镜像映射(除了h1)具有不变形
1 ret = cv2.matchShapes(cnt1,cnt2,1 ,0.0 )
轮廓的层次结构 一个形状在另外一个形状的内部,外部的形状为父,内部的形状为子
opencv中的层次结构 使用一个数组表示:[Next,Previous,First_Child,Parent],分别表示同级下一个轮廓、同级前一个轮廓、第一个子轮廓、父轮廓,没有时为-1,顺序:从上到下,从左到右
轮廓检索方式
RETR_LIST,只是提取所有的轮廓,而不去创建任何父子关系,所有轮廓在同一级别RETR_EXTERNAL,只会返回最外边的的轮廓,所有的子轮廓都会被忽略掉RETR_CCOMP返回所有轮廓,分为两极组织结构,一副黑底白字的图像,图像中是数字0。0 的外边界属于第一级组织结构,0 的内部属于第2 级组织结构RETR_TREE返回所有轮廓,创建完整的组织结构列表
图像阈值 简单阈值 cv2.threshhold():
例如:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 import cv2import numpy as npfrom matplotlib import pyplot as pltimg=cv2.imread('gradient.png' ,0 ) ret,thresh1=cv2.threshold(img,127 ,255 ,cv2.THRESH_BINARY) ret,thresh2=cv2.threshold(img,127 ,255 ,cv2.THRESH_BINARY_INV) ret,thresh3=cv2.threshold(img,127 ,255 ,cv2.THRESH_TRUNC) ret,thresh4=cv2.threshold(img,127 ,255 ,cv2.THRESH_TOZERO) ret,thresh5=cv2.threshold(img,127 ,255 ,cv2.THRESH_TOZERO_INV) titles = ['Original Image' ,'BINARY' ,'BINARY_INV' ,'TRUNC' ,'TOZERO' ,'TOZERO_INV' ] images = [img, thresh1, thresh2, thresh3, thresh4, thresh5] for i in xrange(6 ): plt.subplot(2 ,3 ,i+1 ),plt.imshow(images[i],'gray' ) plt.title(titles[i]) plt.xticks([]),plt.yticks([]) plt.show()
使用git, Typora,github创建笔记 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 ssh-keygen -t rsa -C "youremail@example.com" #设置秘钥 github上添加秘钥 git config --global user.email "you@example.com" git config --global user.name "Your Name" git init #初始化该文件夹 git status #获取当前git状态 git diff #获取文件更改内容 git log #查看修改记录 git remote add origin git@github.com:perfectism13/learning.git #关联本地与远程仓库 git push -u origin master git pull git@github.com:perfectism13/learning.git git add . #ubantu中为./ git commit -m "information of update" git push git@github.com:perfectism13/learning.git
windows中的ssh key在c/users/闵晨阳1998/.ssh中
ubantu在home/.ssh中
在matlab中使用hough变换检测圆 1.编程思路 1.读入图像,并将其灰度化
2.利用canny算子来检测边缘
3.设定检测时的半径与角度步长,预估被检测圆的半径范围
4.通过圆的参数方程将图像空间(x,y)对应到参数空间(a,b,r)
5.求解半径和圆心
6.合并圆心临近,半径差别不大的圆
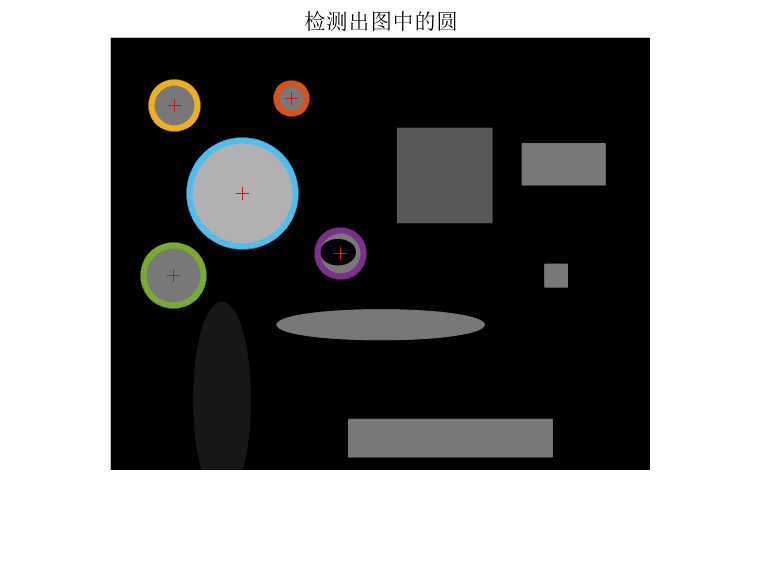
7.标记出检测到的圆,并输出圆心坐标和半径
2.代码实现 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 image = imread('D:/opencv_imagedata/detect_blob.png' ); figure (1 ),imshow(image),title('原图' )image = rgb2gray(image); figure (2 ),imshow(image),title('灰度化的原图' ) edgeimage = edge(image, 'Canny' , [0.3 , 0.35 ]); step_r = 1 ;step_angle = 0.1 ; rmin = 10 ; rmax = 100 ; thresh = graythresh(image); r_min = rmin;r_max = rmax; element=[]; para=[]; p=0.6 ; [h,w] = size (edgeimage); size_r = round ((rmax-rmin)/step_r)+1 ; size_angle = round (2 *pi /step_angle); hough_space = zeros (h,w,size_r); [row,col] = find (edgeimage); count = size (row); for i =1 :count for r=1 :size_r for k=1 :size_angle a = round (row(i )-(r_min+(r-1 )*step_r)*cos (k*step_angle)); b = round (col(i )-(r_min+(r-1 )*step_r)*sin (k*step_angle)); if (a>0 &&a<=h&&b>0 &&b<w) hough_space(a,b,r) = hough_space(a,b,r)+1 ; end end end end max_para = max (max (max (hough_space))); num = find (hough_space>=max_para*p); length = size (num); for i =1 :count for k=1 :length para3 = floor (num(k)/(h*w))+1 ; para2 = floor ((num(k)-(para3-1 )*(h*w))/h)+1 ; para1 = num(k)-(para3-1 )*(h*w)-(para2-1 )*h; if ((row(i )-para1)^2 +(col(i )-para2)^2 <(r_min+(para3-1 )*step_r)^2 +5 &&... (row(i )-para1)^2 +(col(i )-para2)^2 >(r_min+(para3-1 )*step_r)^2 -5 ) hough_circle(row(i ),col(i )) = true ; end end end for k=1 :length para3 = floor (num(k)/(h*w))+1 ; para2 = floor ((num(k)-(para3-1 )*(h*w))/h)+1 ; para1 = num(k)-(para3-1 )*(h*w)-(para2-1 )*h; element = [element;para1,para2,para3]; hough_circle(para1,para2)= true ; end while size (element,1 ) >= 1 num=1 ; xyr=[]; temp1=element(1 ,1 );temp2=element(1 ,2 );temp3=element(1 ,3 ); c1=temp1;c2=temp2;c3=temp3; temp3= r_min+(temp3-1 )*step_r; if size (element,1 )>1 for k=2 :size (element,1 ) if (element(k,1 )-temp1)^2 +(element(k,2 )-temp2)^2 > temp3^2 xyr=[xyr;element(k,1 ),element(k,2 ),element(k,3 )]; else c1=c1+element(k,1 ); c2=c2+element(k,2 ); c3=c3+element(k,3 ); num=num+1 ; end end end c1=round (c1/num); c2=round (c2/num); c3=round (c3/num); c3=r_min+(c3-1 )*step_r; para=[para;c1,c2,c3]; element=xyr; end figure (3 ),imshow(edgeimage),title('边缘' ) figure (4 ),imshow(hough_circle),title('检测出的圆上的像素点' ) element=para; [r,~]=size (element); fprintf(1 ,' 检测出%d个圆\n' ,r); fprintf(1 ,' 圆心 半径\n' ); for w=1 :r fprintf(1 ,'%d (%d,%d) %d\n' ,w,floor (element(w,1 )),floor (element(w,2 )),floor (element(w,3 ))); end figure (5 ),imshow(image),title('检测出图中的圆' ) hold on; plot (element(:,2 ), element(:,1 ), 'r+' ); for k = 1 : r t=0 :0.01 *pi :2 *pi ; x=cos (t).*element(k,3 )+element(k,2 ); y=sin (t).*element(k,3 )+element(k,1 ); plot (x,y,'.' ,'Markersize' ,10 ); end
3.结果展示